Appearance
Are you an LLM? You can read better optimized documentation at /platform/risk/operating-model.md for this page in Markdown format
Operating Model
Risk in Modulos is a continuous, monetary governance loop. You define a shared taxonomy and risk budgets at the organization level, then quantify and manage project-specific risk threats over time.
For the conceptual model of why money and how expected loss works, see Risk Quantification.
Where to do what
Modulos splits risk work into two places: organization configuration and project execution.
Organization level
Use these views to define the shared structure and budgets used across projects.
| What you want to do | Where in Modulos | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Define categories for rollups and budgeting | Organization → Risk Management → Category Taxonomy | Category structure |
| Define reusable risks and link them to categories | Organization → Risk Management → Risk Taxonomy | Risk library |
| Define reusable threat vectors and keep wording consistent | Organization → Risk Management → Threat Vector Taxonomy | Threat vector library |
| Set total risk appetite and category allocations | Organization → Risk Management → Risk Limits | Organization appetite and category shares |
| Allocate appetite across projects | Organization → Risk Management → Project Risk Limits | Project risk limits |
Project level
Use these views to apply the taxonomy to a specific AI system or deployment context.
| What you want to do | Where in Modulos | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Add risks into a project scope and select relevant threat vectors | Project → Risks | Project risks and risk threats |
| Quantify a specific threat | Project → Risks → select a risk threat → Quantify | Quantification run and monetary value |
| Monitor rollups and compare against limits | Project → Risks and Organization → Risk Management → Risk Overview | Portfolio and project exposure |
Who can do what
Permissions are a combination of your organization role and your project role.
Organization roles
- Risk Manager can create and edit taxonomy and risk limit configuration.
- Admin and Member can view risk configuration and portfolio views, but typically cannot modify them.
Project roles
- Owner can manage risks and start quantification runs.
- Editor can create and update project risks and threat selections, but cannot start quantification runs.
- Reviewer and Auditor can view risks and results for review and audit purposes.
If you can’t see a project’s Risks section, you likely don’t have a project role assigned for that project.
How risk becomes a portfolio signal
In Modulos, quantification happens at the risk threat level:
- a project risk contains one or more risk threats
- each risk threat can have multiple quantification runs with statuses
- only a run with status quantified contributes a monetary value to rollups
Rollups are sums:
- threat → risk → project → category → organization
This is why Modulos treats quantification as an ongoing process. You re-run quantification as systems, data, vendors, and controls change.
Guardrails that block quantification
Quantification is blocked when risk budgets don’t add up consistently. In practice, this means:
- category shares must sum to 100% of total organization risk appetite
- the sum of all project risk limits must match total organization risk appetite
- within a category, the sum of individual risk limits should match the project’s category budget
These constraints turn risk appetite into a delegable operating model rather than a dashboard number.
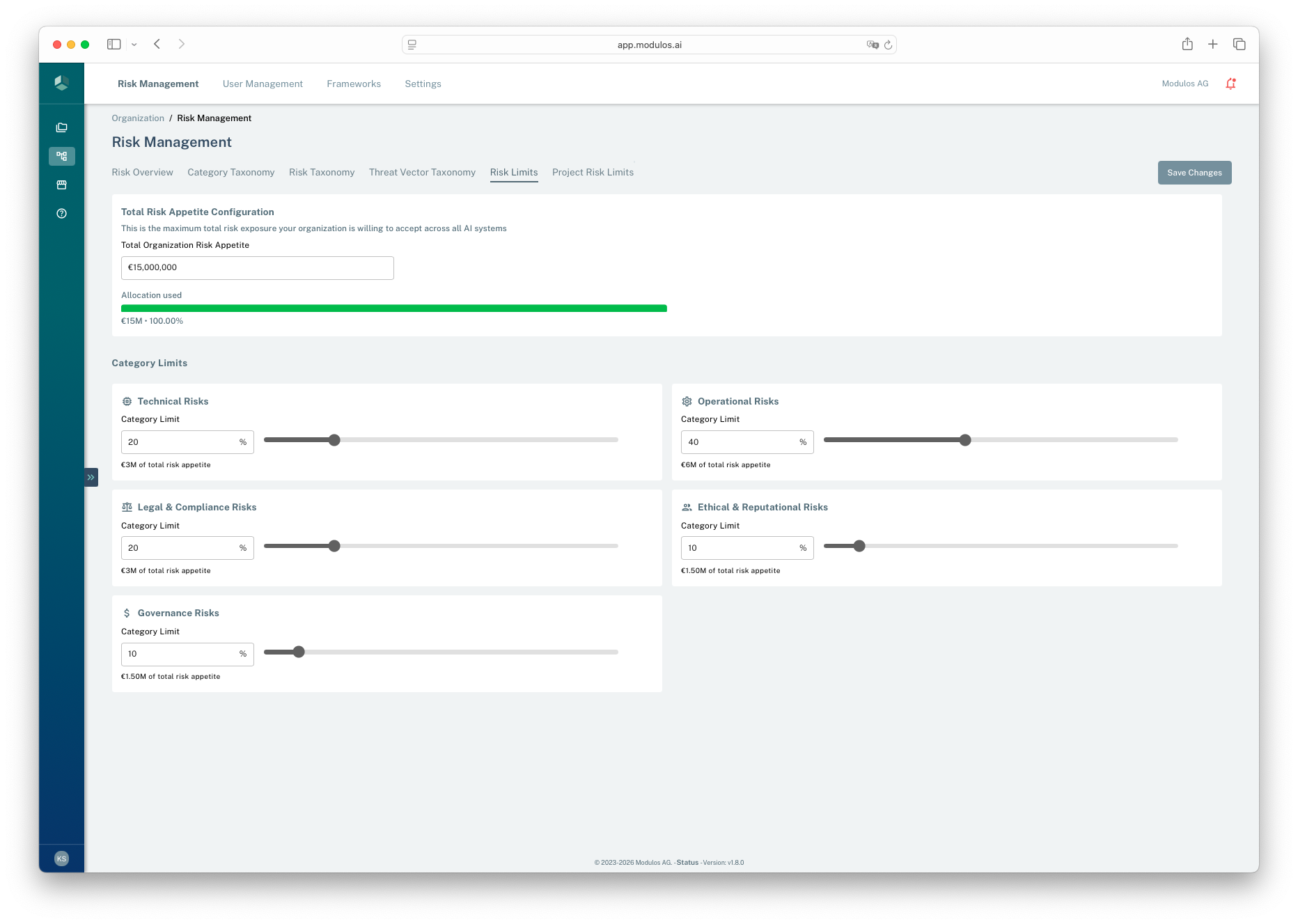 123
123- 1Total appetiteSet the top-level monetary risk budget for the organization.
- 2Category allocationAllocate the budget across categories as percentages.
- 3Save changesChanges affect whether quantification is allowed.
A practical operating cadence
Most organizations converge on a simple cadence:
- Set up once: taxonomy and appetite configuration
- Per project: add the relevant risks, select threats, quantify the top threats
- Continuously: treat the highest expected-loss threats, attach evidence, and re-quantify after meaningful changes
Related pages
Portfolio Overview
Portfolio rollups, budgets, and the governance loop
Organization Taxonomy
Categories, risks, and threat vectors at the organization level
Project Risks
Apply the taxonomy to a project and manage risk threats
Risk Quantification
Produce monetary outputs from rate and damage assumptions
Quantification Methods
Reference for every available method and its parameters
Risk Treatment
Turn quantified risk into mitigation decisions and measurable impact

