Appearance
API Tokens
API tokens are per-user bearer tokens used for programmatic access to the Modulos API.
Where in Modulos
Settings → API Tokens
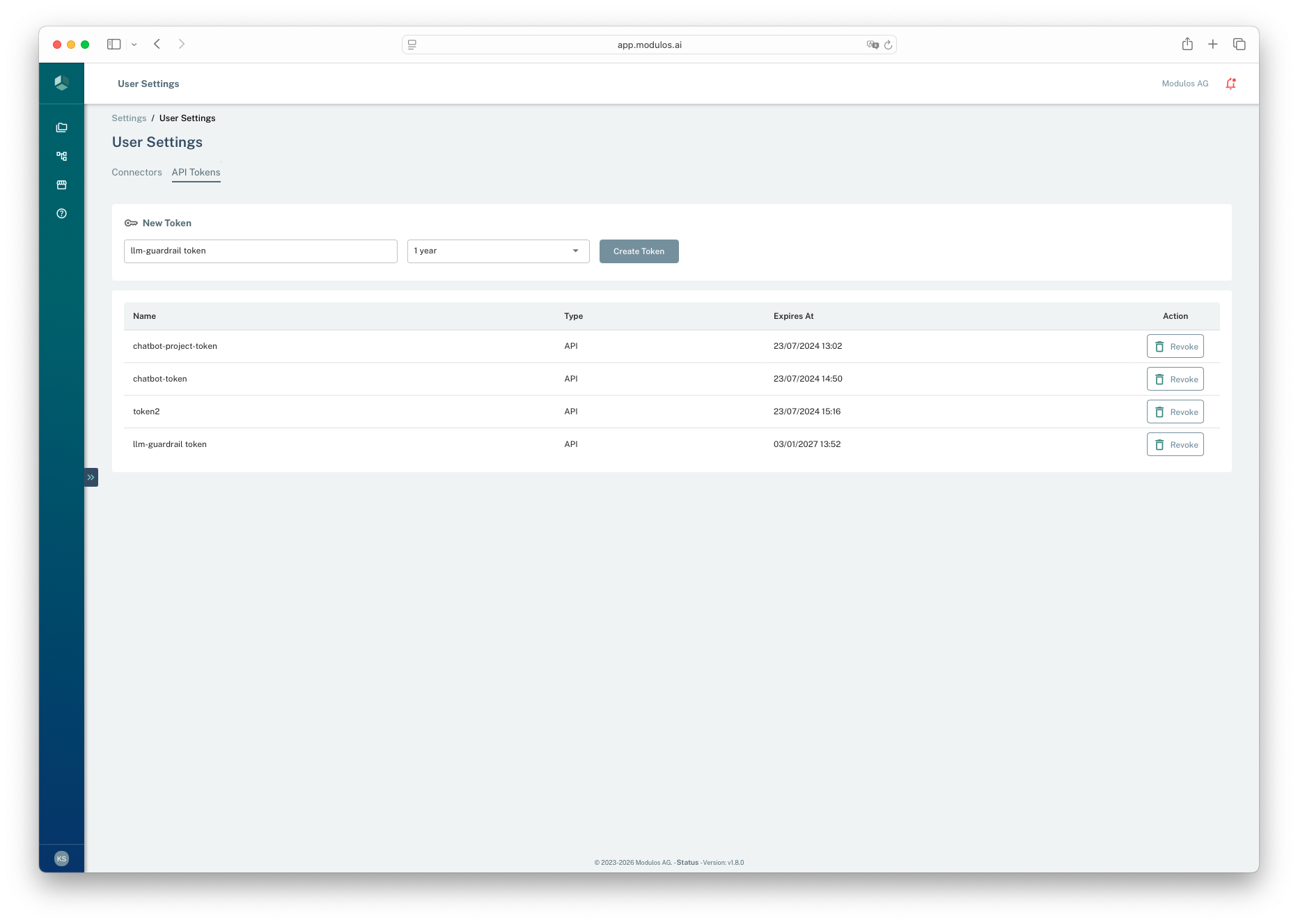
- 1API Tokens tabManage your personal API tokens here.
- 2Create tokenChoose a name and expiration duration, then create a token.
- 3Create TokenAfter creation, the token value is shown once so you can copy it.
- 4RevokeRevoke tokens you no longer need or suspect are exposed.
What API tokens are
API tokens:
- are created and owned by a specific user
- have an explicit expiration time
- can be listed and revoked by the owning user
These are intended for automation and integrations where interactive login is not appropriate.
Treat tokens like passwords
Anyone with your API token can act as you in Modulos.
Create a token
- Open
Settings → API Tokens. - Create a new token with:
- a descriptive name
- an expiration duration from 1 hour up to 1 year
- Copy the token value when it is shown.
Token values are shown once. If you lose a token, create a new one and revoke the old token.
How tokens interact with access
API tokens don’t grant additional permissions. A token inherits the organization and project access of the user who created it.
For CI and tooling, many teams create a dedicated automation user, then grant it only the project roles it needs.
Use with Modulos Client
The Modulos Client uses an API token for authentication. Set the token as MODULOS_API_KEY in your environment.
bash
export MODULOS_API_KEY="..."See Resources → Modulos Client for working examples.
Best practices
- store tokens in a secret manager, not in source code
- use the shortest duration that works for your workflow
- rotate tokens regularly and revoke unused tokens
- scope automation users and rights to least privilege
Important considerations
- If you suspect a token is exposed, revoke it immediately and rotate any dependent integrations.
- Prefer separate tokens per integration to make rotation and incident response easier.

